需扫描的文档

scan.py
import numpy as np import cv2 # 获取四个点 def get_point(pts): rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype="float32") # 按顺序计算四个坐标:左上,右上,右下,左下 s = pts.sum(axis=1) # 左上,右下 rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] # 右上,左下 diff = np.diff(pts, axis=1) rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] return rect def point_transform(image, pts): # 获取输入坐标点 rect = get_point(pts) (tl, tr, br, bl) = rect # 计算输入的w、h widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)) maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB)) heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2)) heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB)) # 变换后的对应坐标位置 dst = np.array([[0, 0], [maxWidth - 1, 0], [maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], [0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype="float32") # 计算变换矩阵 M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (maxWidth, maxHeight)) return warped def resize(image, width=None, height=None, inter=cv2.INTER_AREA): dim = None (h, w) = image.shape[:2] if width is None and height is None: return image if width is None: r = height / float(h) dim = (int(w * r), height) else: r = width / float(w) dim = (width, int(h * r)) resized = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=inter) return resized # 读取文档 image = cv2.imread("images/document_1.jpg") ratio = image.shape[0] / 500.0 image_copy = image.copy() image = resize(image_copy, height=500) # 灰度处理 gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 高斯处理 gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0) edged = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150) # 预处理完的结果 cv2.imshow("Image", image) cv2.imshow("Edged", edged) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() # 轮廓检测 screenCnt = None cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[1] cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[:5] for c in cnts: # 计算近似轮廓 peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True) # 参数说明:输入的点集、准确度(从原始轮廓到近似轮廓的最大距离)、是否封闭 approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True) if len(approx) == 4: screenCnt = approx break # 绘制轮廓 cv2.drawContours(image, [screenCnt], -1, (2, 255, 0), 2) cv2.imshow("image", image) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() # 透视变换(二维源图 ---> 三维 ---> 二维) warped = point_transform(image_copy, screenCnt.reshape(4, 2) * ratio) # 二值处理 warped = cv2.cvtColor(warped, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ref = cv2.threshold(warped, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1] cv2.imwrite("scan.jpg", ref) # 输出结果 cv2.imshow("origin", resize(image_copy, height=500)) cv2.imshow("result", resize(ref, height=500)) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()扫描结果
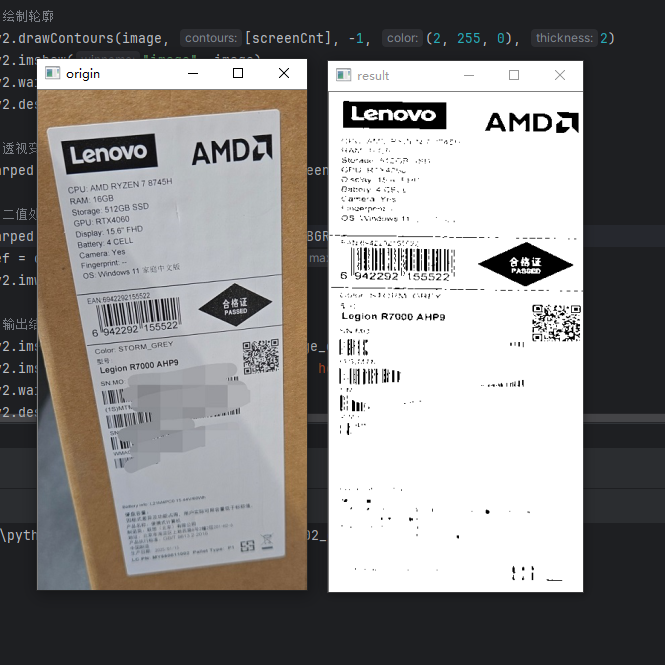
流程说明
- 边缘检测
- 获取轮廓
- 变换
版权属于:
suaxi
作品采用:
《
署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
》许可协议授权


评论 (0)