搜索到
51
篇与
的结果
-
 Lock(锁) Lock(锁)从Jdk5开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制——通过显式定义同步锁对象来实现同步(同步锁使用Lock对象充当)java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具;锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显示加锁,释放锁使用方法:class A{ //定义锁 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public void method() { lock.lock(); //加锁 try { //保证线程安全的代码 }finally { lock.unlock(); //解锁 //如果同步代码有异常,要将unlock()写入finally语句块 } } } }购票实例:package com.thread.threadDemo; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 18:09 * 测试Lock锁 */ public class TestLock { public static void main(String[] args) { TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); } } class TestLock2 implements Runnable{ int ticketNums = 10; //定义锁 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { while (true){ lock.lock(); //加锁 try { if (ticketNums>0){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(ticketNums--); }else { break; } }finally { lock.unlock(); //解锁 } } } }synchronized与Lock对比1、Lock是显示锁(手动开启和关闭);synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放2、Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁3、使用Lock锁时,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,并且具有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类)4、优先使用顺序:Lock --->同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源) --->同步方法(在方法体之外)
Lock(锁) Lock(锁)从Jdk5开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制——通过显式定义同步锁对象来实现同步(同步锁使用Lock对象充当)java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具;锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显示加锁,释放锁使用方法:class A{ //定义锁 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public void method() { lock.lock(); //加锁 try { //保证线程安全的代码 }finally { lock.unlock(); //解锁 //如果同步代码有异常,要将unlock()写入finally语句块 } } } }购票实例:package com.thread.threadDemo; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 18:09 * 测试Lock锁 */ public class TestLock { public static void main(String[] args) { TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); } } class TestLock2 implements Runnable{ int ticketNums = 10; //定义锁 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { while (true){ lock.lock(); //加锁 try { if (ticketNums>0){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(ticketNums--); }else { break; } }finally { lock.unlock(); //解锁 } } } }synchronized与Lock对比1、Lock是显示锁(手动开启和关闭);synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放2、Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁3、使用Lock锁时,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,并且具有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类)4、优先使用顺序:Lock --->同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源) --->同步方法(在方法体之外) -
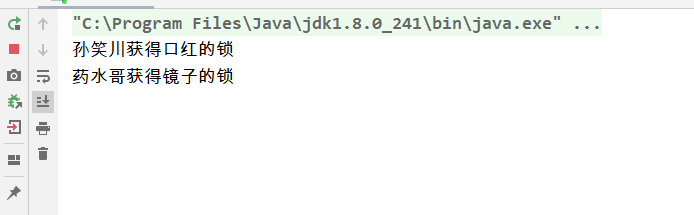
 死锁 死锁定义:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持产生死锁的四个必要条件:1、互斥:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用2、请求与保持:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放3、不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺4、循环等待:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系死锁实例:package com.thread.threadDemo; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 16:18 * 死锁:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { MakeUp p1 = new MakeUp(0, "孙笑川"); MakeUp p2 = new MakeUp(1, "药水哥"); p1.start(); p2.start(); } } //口红 class Lipstick{ } //镜子 class Mirror{ } class MakeUp extends Thread{ //需要的资源只有一份,用statick来保证只有一份 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); int choice; //选择 String name; //使用人 public MakeUp(int choice,String name){ this.choice = choice; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { //化妆 try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if (choice==0){ synchronized (lipstick){ //拿到口红 System.out.println(this.name+"获得口红的锁"); Thread.sleep(1000); synchronized (mirror){ //等待一秒后想拿镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); } } }else { synchronized (mirror){//拿到镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); Thread.sleep(2000); synchronized (lipstick) { //等待两秒后想拿口红 System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁"); } } } } }将choice==0中的synchronized (mirror)拿到synchronized (lipStick)之外,else中的代码同理,即可解决实例中的死锁问题package com.thread.threadDemo; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 16:18 * 死锁:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { MakeUp p1 = new MakeUp(0, "孙笑川"); MakeUp p2 = new MakeUp(1, "药水哥"); p1.start(); p2.start(); } } //口红 class Lipstick{ } //镜子 class Mirror{ } class MakeUp extends Thread{ //需要的资源只有一份,用statick来保证只有一份 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); int choice; //选择 String name; //使用人 public MakeUp(int choice,String name){ this.choice = choice; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { //化妆 try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if (choice==0){ synchronized (lipstick){ //拿到口红 System.out.println(this.name+"获得口红的锁"); Thread.sleep(1000); } synchronized (mirror){ //等待一秒后想拿镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); } }else { synchronized (mirror){//拿到镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); Thread.sleep(2000); } synchronized (lipstick) { //等待两秒后想拿口红 System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁"); } } } }
死锁 死锁定义:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持产生死锁的四个必要条件:1、互斥:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用2、请求与保持:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放3、不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺4、循环等待:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系死锁实例:package com.thread.threadDemo; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 16:18 * 死锁:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { MakeUp p1 = new MakeUp(0, "孙笑川"); MakeUp p2 = new MakeUp(1, "药水哥"); p1.start(); p2.start(); } } //口红 class Lipstick{ } //镜子 class Mirror{ } class MakeUp extends Thread{ //需要的资源只有一份,用statick来保证只有一份 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); int choice; //选择 String name; //使用人 public MakeUp(int choice,String name){ this.choice = choice; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { //化妆 try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if (choice==0){ synchronized (lipstick){ //拿到口红 System.out.println(this.name+"获得口红的锁"); Thread.sleep(1000); synchronized (mirror){ //等待一秒后想拿镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); } } }else { synchronized (mirror){//拿到镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); Thread.sleep(2000); synchronized (lipstick) { //等待两秒后想拿口红 System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁"); } } } } }将choice==0中的synchronized (mirror)拿到synchronized (lipStick)之外,else中的代码同理,即可解决实例中的死锁问题package com.thread.threadDemo; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 16:18 * 死锁:多个线程互相拥抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { MakeUp p1 = new MakeUp(0, "孙笑川"); MakeUp p2 = new MakeUp(1, "药水哥"); p1.start(); p2.start(); } } //口红 class Lipstick{ } //镜子 class Mirror{ } class MakeUp extends Thread{ //需要的资源只有一份,用statick来保证只有一份 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); int choice; //选择 String name; //使用人 public MakeUp(int choice,String name){ this.choice = choice; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { //化妆 try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if (choice==0){ synchronized (lipstick){ //拿到口红 System.out.println(this.name+"获得口红的锁"); Thread.sleep(1000); } synchronized (mirror){ //等待一秒后想拿镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); } }else { synchronized (mirror){//拿到镜子 System.out.println(this.name+"获得镜子的锁"); Thread.sleep(2000); } synchronized (lipstick) { //等待两秒后想拿口红 System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁"); } } } } -
 线程同步 线程同步由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突问题,为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制 synchronized,当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用释放锁即可,但同时也会带来如下问题:一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起在多线程竞争下,加锁、释放锁会导致频繁的 上下文切换 和 调度延时,引起性能问题如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁,会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题同步方法synchronized关键字包括synchronized方法和synchronized块两种方法同步方法 public synchronized void method(int args){}synchronized方法控制对象的访问,每个对象对应一把锁,每个synchronized方法都必须获得调用该方法的对象的锁才能执行,否则线程会阻塞,方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到该方法返回才释放锁,后面被阻塞的线程才能获得这个锁,继续执行同步块同步块 synchronized(Obj){}(Obj){}同步监视器Obj可以是任何对象,推荐使用共享资源作为同步监视器同步方法中无须指定同步监视器,因为同步方法的同步监视器就是这个对象本身,或者是class执行过程第一个线程访问,锁定同步监视器,执行其中代码第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器被锁定,无法访问第一个线程访问完毕,释放同步监视器锁第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器没有锁,锁定并进行访问买票问题package com.thread.syn; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 14:40 * 不安全的买票,结果中出现负的票数 */ public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(buyTicket,"孙笑川").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"药水哥").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"Giao哥").start(); } } class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ //票 private int ticketNums = 10; //外部停止标志 boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { while (flag){ try { buy(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //synchronized同步方法 private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException { //判断是否有票 if (ticketNums<=0){ flag = false; return; } //模拟延时 Thread.sleep(100); //买票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到了票"+ticketNums--); } }模拟取款package com.thread.syn; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 15:03 */ public class UnsafeBank { public static void main(String[] args) { //账户 Account account = new Account(100, "存折"); Drawing sun = new Drawing(account, 50, "孙笑川"); Drawing yao = new Drawing(account, 100, "药水哥"); sun.start(); yao.start(); } } //账户 class Account{ int money; //余额 String name; //账户名 public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } } //银行:模拟取款 class Drawing extends Thread{ Account account; //账户 int drawingMoney; //取款额度 int cash; //现金 public Drawing(Account account,int drawingMoney,String name){ super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } //取钱 //synchronized 默认锁的是this. @Override public void run() { //synchronized锁的对象就是变化的量,即需要增删改的对象 synchronized (account){ //判断余额 if (account.money-drawingMoney<0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"账户余额不足"); return; } //sleep可以放大问题的发生性 try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //余额 = 卡内余额 - 取款额度 account.money = account.money - drawingMoney; //现金 cash = cash + drawingMoney; System.out.println(account.name+"账户余额:"+account.money); //继承Thread类,所以此处的this.getName() = Thread.currentThread().getName() System.out.println(this.getName()+"现金:"+cash); } } }线程不安全的集合package com.thread.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 14:59 * 线程不安全的集合 */ public class UnsafeList { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ synchronized (list){ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } } 补充:JUC安全类型的集合CopyOnWriteArrayListpackage com.thread.syn; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 15:48 * 测试JUC安全类型的集合 */ public class TestJUC { public static void main(String[] args) { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } }
线程同步 线程同步由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突问题,为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制 synchronized,当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用释放锁即可,但同时也会带来如下问题:一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起在多线程竞争下,加锁、释放锁会导致频繁的 上下文切换 和 调度延时,引起性能问题如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁,会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题同步方法synchronized关键字包括synchronized方法和synchronized块两种方法同步方法 public synchronized void method(int args){}synchronized方法控制对象的访问,每个对象对应一把锁,每个synchronized方法都必须获得调用该方法的对象的锁才能执行,否则线程会阻塞,方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到该方法返回才释放锁,后面被阻塞的线程才能获得这个锁,继续执行同步块同步块 synchronized(Obj){}(Obj){}同步监视器Obj可以是任何对象,推荐使用共享资源作为同步监视器同步方法中无须指定同步监视器,因为同步方法的同步监视器就是这个对象本身,或者是class执行过程第一个线程访问,锁定同步监视器,执行其中代码第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器被锁定,无法访问第一个线程访问完毕,释放同步监视器锁第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器没有锁,锁定并进行访问买票问题package com.thread.syn; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 14:40 * 不安全的买票,结果中出现负的票数 */ public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(buyTicket,"孙笑川").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"药水哥").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"Giao哥").start(); } } class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ //票 private int ticketNums = 10; //外部停止标志 boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { while (flag){ try { buy(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //synchronized同步方法 private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException { //判断是否有票 if (ticketNums<=0){ flag = false; return; } //模拟延时 Thread.sleep(100); //买票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到了票"+ticketNums--); } }模拟取款package com.thread.syn; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 15:03 */ public class UnsafeBank { public static void main(String[] args) { //账户 Account account = new Account(100, "存折"); Drawing sun = new Drawing(account, 50, "孙笑川"); Drawing yao = new Drawing(account, 100, "药水哥"); sun.start(); yao.start(); } } //账户 class Account{ int money; //余额 String name; //账户名 public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } } //银行:模拟取款 class Drawing extends Thread{ Account account; //账户 int drawingMoney; //取款额度 int cash; //现金 public Drawing(Account account,int drawingMoney,String name){ super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } //取钱 //synchronized 默认锁的是this. @Override public void run() { //synchronized锁的对象就是变化的量,即需要增删改的对象 synchronized (account){ //判断余额 if (account.money-drawingMoney<0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"账户余额不足"); return; } //sleep可以放大问题的发生性 try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //余额 = 卡内余额 - 取款额度 account.money = account.money - drawingMoney; //现金 cash = cash + drawingMoney; System.out.println(account.name+"账户余额:"+account.money); //继承Thread类,所以此处的this.getName() = Thread.currentThread().getName() System.out.println(this.getName()+"现金:"+cash); } } }线程不安全的集合package com.thread.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 14:59 * 线程不安全的集合 */ public class UnsafeList { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ synchronized (list){ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } } 补充:JUC安全类型的集合CopyOnWriteArrayListpackage com.thread.syn; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 15:48 * 测试JUC安全类型的集合 */ public class TestJUC { public static void main(String[] args) { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } } -
 守护线程 守护(Daemon)线程分为用户线程和守护线程虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕例:后台记录操作日志,内存监控,垃圾回收等package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 11:26 * 守护线程 */ public class TestDaemon { public static void main(String[] args) { God god = new God(); You you = new You(); Thread thread = new Thread(god); thread.setDaemon(true); //默认为false表示用户线程,正常的线程都是用户线程 thread.start(); //启动上帝线程 new Thread(you).start(); } } //上帝 class God implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { while (true){ System.out.println("God bless you!"); } } } //人 class You implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) { System.out.println("还活着!"); } System.out.println("原地去世了!"); } }
守护线程 守护(Daemon)线程分为用户线程和守护线程虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕例:后台记录操作日志,内存监控,垃圾回收等package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 11:26 * 守护线程 */ public class TestDaemon { public static void main(String[] args) { God god = new God(); You you = new You(); Thread thread = new Thread(god); thread.setDaemon(true); //默认为false表示用户线程,正常的线程都是用户线程 thread.start(); //启动上帝线程 new Thread(you).start(); } } //上帝 class God implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { while (true){ System.out.println("God bless you!"); } } } //人 class You implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) { System.out.println("还活着!"); } System.out.println("原地去世了!"); } } -
 线程优先级 线程优先级Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度按照优先级来调度执行线程优先级范围:1~10Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10设置方法注:1、线程优先级应先设置再启动 2、优先级低只意味着获得调度的概率低,并不是优先级低就不会被调用,最终结果由CPU调度决定package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 11:11 * 测试线程优先级 */ public class TestPriority { public static void main(String[] args) { //主线程默认优先级 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); //设置优先级 Mypeiority mypeiority = new Mypeiority(); Thread t1 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t2 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t3 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t4 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t5 = new Thread(mypeiority); //先设置,再启动 t1.start(); t2.setPriority(3); t2.start(); t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //MAX_PRIORITY=10 t3.start(); t4.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t4.start(); t5.setPriority(7); t5.start(); } } class Mypeiority implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); } }
线程优先级 线程优先级Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度按照优先级来调度执行线程优先级范围:1~10Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10设置方法注:1、线程优先级应先设置再启动 2、优先级低只意味着获得调度的概率低,并不是优先级低就不会被调用,最终结果由CPU调度决定package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/26 11:11 * 测试线程优先级 */ public class TestPriority { public static void main(String[] args) { //主线程默认优先级 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); //设置优先级 Mypeiority mypeiority = new Mypeiority(); Thread t1 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t2 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t3 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t4 = new Thread(mypeiority); Thread t5 = new Thread(mypeiority); //先设置,再启动 t1.start(); t2.setPriority(3); t2.start(); t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //MAX_PRIORITY=10 t3.start(); t4.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t4.start(); t5.setPriority(7); t5.start(); } } class Mypeiority implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); } } -
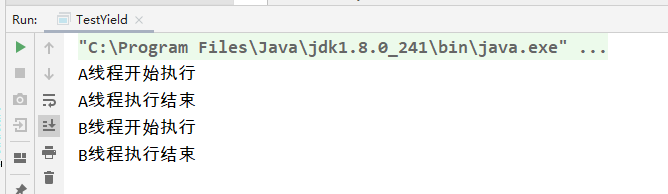
 线程礼让 线程礼让Thread.yield();实例:package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/25 21:31 */ public class TestYield { public static void main(String[] args) { MyYield myYield = new MyYield(); new Thread(myYield,"A").start(); new Thread(myYield,"B").start(); } } class MyYield implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行"); Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程执行结束"); } }注:礼让的结果最终由CPU调度决定
线程礼让 线程礼让Thread.yield();实例:package com.thread.state; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/25 21:31 */ public class TestYield { public static void main(String[] args) { MyYield myYield = new MyYield(); new Thread(myYield,"A").start(); new Thread(myYield,"B").start(); } } class MyYield implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行"); Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程执行结束"); } }注:礼让的结果最终由CPU调度决定 -
 线程休眠 线程休眠sleep(时间)指当前线程阻塞的毫秒数sleep存在异常InterruptedExceptionsleep时间达到后线程进入就绪状态可以模拟网络延时,倒计时等每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁模拟倒计时实例:package com.thread.state; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/25 17:24 */ public class TestSleep2 { public static void main(String[] args){ //tenDown(); //打印当前系统时间 Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); while (true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date)); date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); //更新当前系统时间 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //模拟倒计时 public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException { int num = 10; while (true){ Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(num--); if (num<=0){ break; } } } }
线程休眠 线程休眠sleep(时间)指当前线程阻塞的毫秒数sleep存在异常InterruptedExceptionsleep时间达到后线程进入就绪状态可以模拟网络延时,倒计时等每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁模拟倒计时实例:package com.thread.state; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2020/11/25 17:24 */ public class TestSleep2 { public static void main(String[] args){ //tenDown(); //打印当前系统时间 Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); while (true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date)); date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); //更新当前系统时间 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //模拟倒计时 public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException { int num = 10; while (true){ Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(num--); if (num<=0){ break; } } } } -