搜索到
463
篇与
的结果
-
 6.查询 查询//查询 @Test void findByIdTest(){ User user = userMapper.selectById(1); System.out.println(user); } //批量查询 @Test void findTest(){ List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4)); users.forEach(System.out::println); //SELECT id,name,age,email,version,create_time,update_time FROM user WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? , ? ) } //条件查询(map) @Test void findTestByMap(){ Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name","刘波"); List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map); users.forEach(System.out::println); }
6.查询 查询//查询 @Test void findByIdTest(){ User user = userMapper.selectById(1); System.out.println(user); } //批量查询 @Test void findTest(){ List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4)); users.forEach(System.out::println); //SELECT id,name,age,email,version,create_time,update_time FROM user WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? , ? ) } //条件查询(map) @Test void findTestByMap(){ Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name","刘波"); List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map); users.forEach(System.out::println); } -
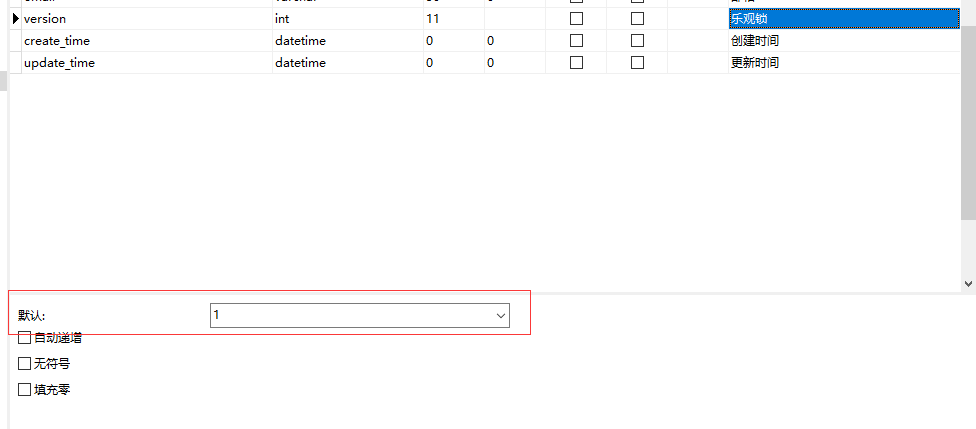
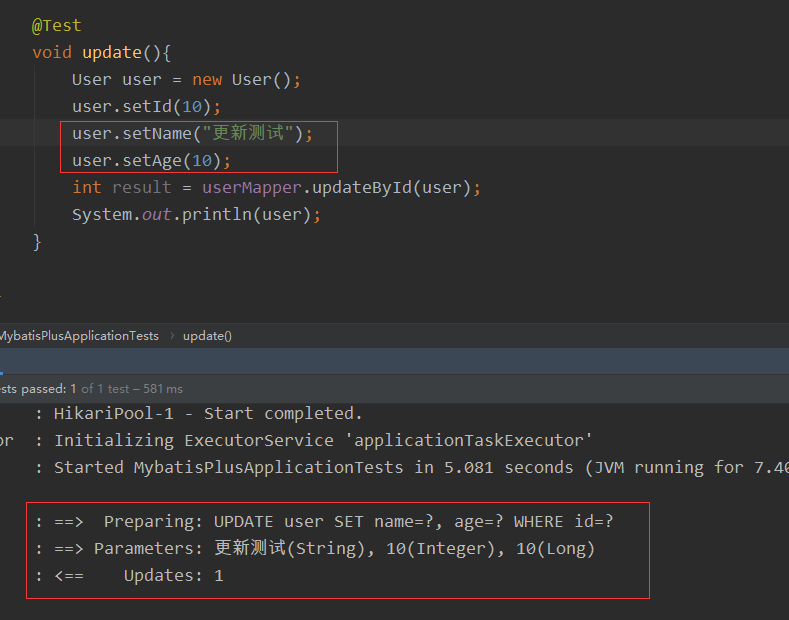
 5.乐观锁 乐观锁乐观锁实现方式:取出记录时,获取当前version更新时,带上这个version执行更新时, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion如果version不对,就更新失败--A线程 update user set name = 'test',version = version + 1 where id = 1 and version = 1; --B线程(此时如果B线程抢先完成修改操作,则A线程会执行失败) update user set name = 'test',version = version + 1 where id = 1 and version = 1;乐观锁插件测试1.数据库增加version字段,并设置默认值为12.实体类@Version private int version;3.注册组件package com.sw.mybatisplus.config; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.OptimisticLockerInterceptor; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/5 11:48 */ @EnableTransactionManagement @Configuration public class MyBatisPlusConfig { //注册乐观锁插件 @Bean public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor(){ return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor(); } } 4.单元测试 @Test void update(){ User user = new User(); user.setId(11); user.setName("自动填充测试"); user.setAge(30); int result = userMapper.updateById(user); System.out.println(result); } //测试乐观锁(成功) @Test void OptimisticLockerInterceptorTest1(){ //1.查询用户信息 User user = userMapper.selectById(10L); //2.修改信息 user.setName("乐观锁测试01"); //3.执行更新 userMapper.updateById(user); } //测试乐观锁(失败)(模拟多线程) @Test void OptimisticLockerInterceptorTest2(){ User user = userMapper.selectById(10L); user.setName("乐观锁测试111"); //模拟插队 User user1 = userMapper.selectById(10L); user1.setName("乐观锁测试222"); userMapper.updateById(user1); //自旋锁尝试多次提交 userMapper.updateById(user); }
5.乐观锁 乐观锁乐观锁实现方式:取出记录时,获取当前version更新时,带上这个version执行更新时, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion如果version不对,就更新失败--A线程 update user set name = 'test',version = version + 1 where id = 1 and version = 1; --B线程(此时如果B线程抢先完成修改操作,则A线程会执行失败) update user set name = 'test',version = version + 1 where id = 1 and version = 1;乐观锁插件测试1.数据库增加version字段,并设置默认值为12.实体类@Version private int version;3.注册组件package com.sw.mybatisplus.config; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.OptimisticLockerInterceptor; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/5 11:48 */ @EnableTransactionManagement @Configuration public class MyBatisPlusConfig { //注册乐观锁插件 @Bean public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor(){ return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor(); } } 4.单元测试 @Test void update(){ User user = new User(); user.setId(11); user.setName("自动填充测试"); user.setAge(30); int result = userMapper.updateById(user); System.out.println(result); } //测试乐观锁(成功) @Test void OptimisticLockerInterceptorTest1(){ //1.查询用户信息 User user = userMapper.selectById(10L); //2.修改信息 user.setName("乐观锁测试01"); //3.执行更新 userMapper.updateById(user); } //测试乐观锁(失败)(模拟多线程) @Test void OptimisticLockerInterceptorTest2(){ User user = userMapper.selectById(10L); user.setName("乐观锁测试111"); //模拟插队 User user1 = userMapper.selectById(10L); user1.setName("乐观锁测试222"); userMapper.updateById(user1); //自旋锁尝试多次提交 userMapper.updateById(user); } -
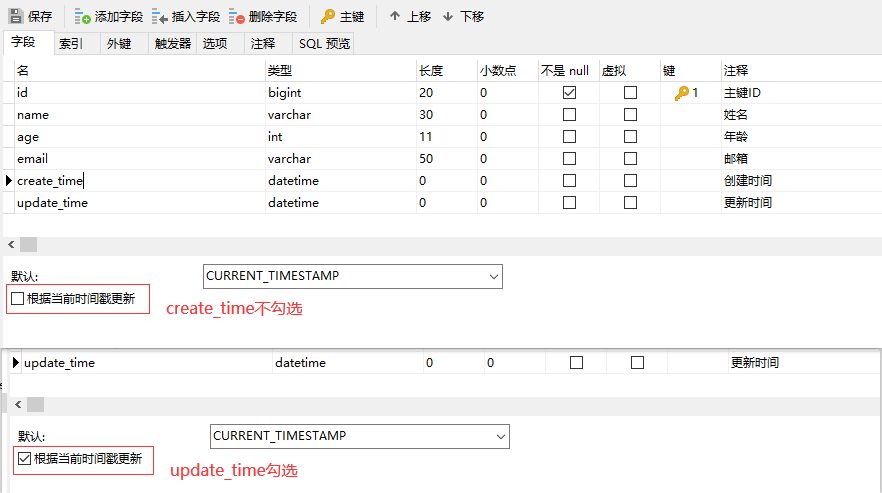
 4.自动填充 自动填充数据库级别1.数据库新增字段,并设置2.实体类添加数据库新增的时间字段3.执行更新操作后查看结果代码级别1.删除数据库的默认值、自动更新操作2.实体类字段属性上增加相应的注解@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Date createTime; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.UPDATE) private Date updateTime;3.元数据处理器package com.sw.mybatisplus.handler; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/5 11:14 * 元数据处理器 */ @Slf4j @Component public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler { //插入时填充策略 @Override public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("start insert fill"); this.setFieldValByName("createTime", new Date(), metaObject); this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject); } @Override public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("start update fill"); this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject); } } 4.执行插入、更新测试后查看数据库
4.自动填充 自动填充数据库级别1.数据库新增字段,并设置2.实体类添加数据库新增的时间字段3.执行更新操作后查看结果代码级别1.删除数据库的默认值、自动更新操作2.实体类字段属性上增加相应的注解@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Date createTime; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.UPDATE) private Date updateTime;3.元数据处理器package com.sw.mybatisplus.handler; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/5 11:14 * 元数据处理器 */ @Slf4j @Component public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler { //插入时填充策略 @Override public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("start insert fill"); this.setFieldValByName("createTime", new Date(), metaObject); this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject); } @Override public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("start update fill"); this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject); } } 4.执行插入、更新测试后查看数据库 -

-
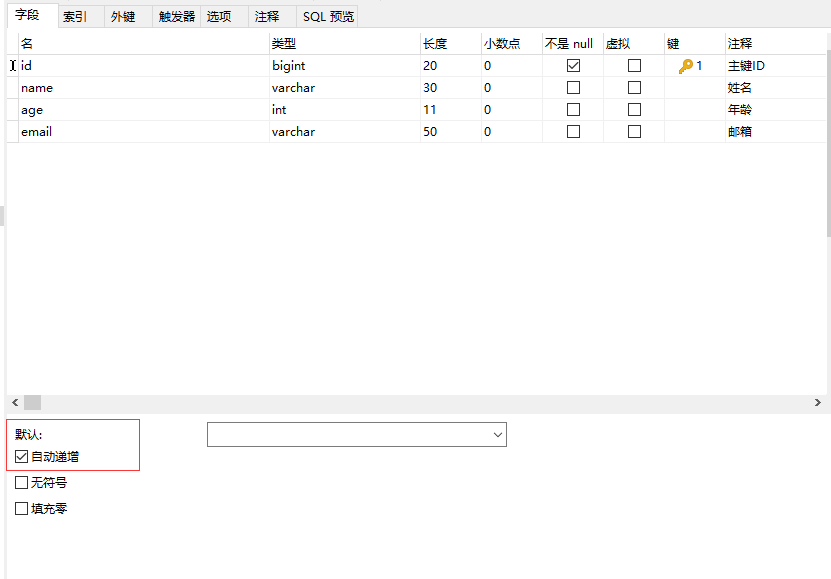
 2.主键生成策略 主键生成策略ID_WORKER 全局唯一ID(默认)雪花算法:snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,类型为long。其核心思想为:使用41bit作为毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit是机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号,最后一位是符号位,永远为0AUTO 主键自增在实体类ID主键上配置: @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)同时数据库也许设置ID自增:IdType类型:public enum IdType { AUTO(0), //主键自增 NONE(1), //无 INPUT(2), //用户自行输入 ID_WORKER(3), //全局唯一(默认) UUID(4), //UUID ID_WORKER_STR(5); //分布式全局唯一ID注:mybatis-plus新版已不再推荐使用 ID_WORK
2.主键生成策略 主键生成策略ID_WORKER 全局唯一ID(默认)雪花算法:snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,类型为long。其核心思想为:使用41bit作为毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit是机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号,最后一位是符号位,永远为0AUTO 主键自增在实体类ID主键上配置: @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)同时数据库也许设置ID自增:IdType类型:public enum IdType { AUTO(0), //主键自增 NONE(1), //无 INPUT(2), //用户自行输入 ID_WORKER(3), //全局唯一(默认) UUID(4), //UUID ID_WORKER_STR(5); //分布式全局唯一ID注:mybatis-plus新版已不再推荐使用 ID_WORK -
 1.插入操作 CRUD实例测试1.新建数据库DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user; CREATE TABLE user ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄', email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', PRIMARY KEY (id) ); INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');2.导入依赖尽量不要同时导入mybatis和mybatis-plus,可能存在版本差异的问题<!--mybatis-plus--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.0.5</version> </dependency>3.插入pojopackage com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo; import lombok.Data; import java.io.Serializable; @Data public class User implements Serializable { private long id; private String name; private int age; private String email; } mapperpackage com.sw.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/4 14:46 */ @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { } Junit单元测试package com.sw.mybatisplus; import com.sw.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper; import com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.util.List; @SpringBootTest class MybatisPlusApplicationTests { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test void contextLoads() { //此处的参数是一个Wrapper(条件构造器) List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(null); userList.forEach(System.out::println); } } 控制台打印sql# 在application.yml配置文件中添加 mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 或者 logging: level: com.xxx.xxx.mapper: debug插入@Test void insertTest(){ User user = new User(); user.setName("孙笑川"); user.setAge(33); user.setEmail("123321@qq.com"); int result = userMapper.insert(user); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(user); //插入时没有手动设置,但此处的打印结果自动回填了id的值 //User(id=0, name=孙笑川, age=33, email=123321@qq.com) }
1.插入操作 CRUD实例测试1.新建数据库DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user; CREATE TABLE user ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄', email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', PRIMARY KEY (id) ); INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');2.导入依赖尽量不要同时导入mybatis和mybatis-plus,可能存在版本差异的问题<!--mybatis-plus--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.0.5</version> </dependency>3.插入pojopackage com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo; import lombok.Data; import java.io.Serializable; @Data public class User implements Serializable { private long id; private String name; private int age; private String email; } mapperpackage com.sw.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /** * @Author suaxi * @Date 2021/4/4 14:46 */ @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { } Junit单元测试package com.sw.mybatisplus; import com.sw.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper; import com.sw.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.util.List; @SpringBootTest class MybatisPlusApplicationTests { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test void contextLoads() { //此处的参数是一个Wrapper(条件构造器) List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(null); userList.forEach(System.out::println); } } 控制台打印sql# 在application.yml配置文件中添加 mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 或者 logging: level: com.xxx.xxx.mapper: debug插入@Test void insertTest(){ User user = new User(); user.setName("孙笑川"); user.setAge(33); user.setEmail("123321@qq.com"); int result = userMapper.insert(user); System.out.println(result); System.out.println(user); //插入时没有手动设置,但此处的打印结果自动回填了id的值 //User(id=0, name=孙笑川, age=33, email=123321@qq.com) } -
 MyBatis-Plus MyBatis-Plus特性无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库内置性能分析插件:可输出 Sql 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
MyBatis-Plus MyBatis-Plus特性无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库内置性能分析插件:可输出 Sql 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作 -
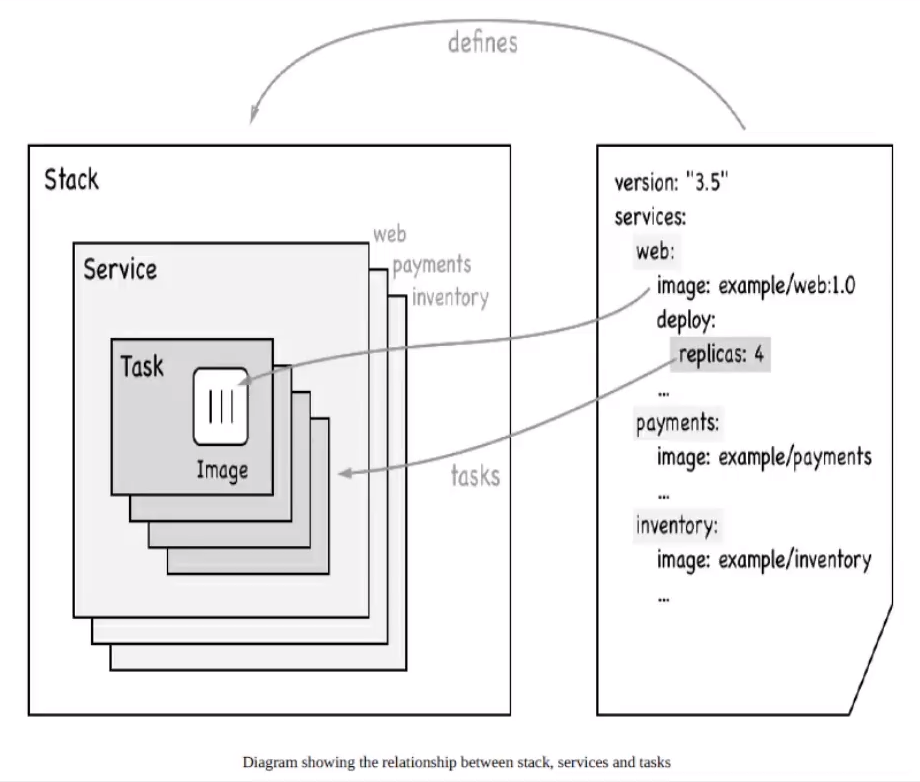
 Docker Swarm Docker Swarm初始化节点:docker swarm init加入节点:docker swarm join# 获取令牌 docker swarm join-token manager # leader docker swarm join-token worker # worker节点信息:Raft协议保证大多数节点存活才可使用,只要>1就可以,集群至少大于3台测试(双主双从):1.docker-1宕机,另一个主节点也不可用2.docker swarm leave 节点离开集群3.集群中的worker节点无法使用manager命令,管理工作一律由manager主节点执行注:至少保证1台管理节点存活docker service --help灰度发布(金丝雀发布)docker run # 容器启动,不具备扩缩容功能 docker service # 以服务的形式发布,可以扩缩容,滚动更新当单个Nginx服务负载较大时,需增加3个服务docker service update --replicas 3 mynginx==只要是一个服务,在集群中的任意一个节点都可以访问,服务可以由多个副本动态扩缩容来实现高可用==移除服务:docker service rm [服务名]小结Swarm:集群的管理和编号Node:docker节点,多个节点组成一个网络集群(分为管理和工作者)Service:服务,可以在管理节点或工作节点运行(compose的核心)Task:容器中的命令(细节任务)service运行模式--mode string # default "replicated" 默认运行于副本节点 docker service create --mode replicated --name test01 centos:7.6 # 运行在副本(默认) docker service create --mode global --name test01 centos:7.6 # 全局节点运行网络模式 PublishMode: ingressSwarmOverlayingress:Overlay的特殊模式,负载均衡(IPVS VIP)
Docker Swarm Docker Swarm初始化节点:docker swarm init加入节点:docker swarm join# 获取令牌 docker swarm join-token manager # leader docker swarm join-token worker # worker节点信息:Raft协议保证大多数节点存活才可使用,只要>1就可以,集群至少大于3台测试(双主双从):1.docker-1宕机,另一个主节点也不可用2.docker swarm leave 节点离开集群3.集群中的worker节点无法使用manager命令,管理工作一律由manager主节点执行注:至少保证1台管理节点存活docker service --help灰度发布(金丝雀发布)docker run # 容器启动,不具备扩缩容功能 docker service # 以服务的形式发布,可以扩缩容,滚动更新当单个Nginx服务负载较大时,需增加3个服务docker service update --replicas 3 mynginx==只要是一个服务,在集群中的任意一个节点都可以访问,服务可以由多个副本动态扩缩容来实现高可用==移除服务:docker service rm [服务名]小结Swarm:集群的管理和编号Node:docker节点,多个节点组成一个网络集群(分为管理和工作者)Service:服务,可以在管理节点或工作节点运行(compose的核心)Task:容器中的命令(细节任务)service运行模式--mode string # default "replicated" 默认运行于副本节点 docker service create --mode replicated --name test01 centos:7.6 # 运行在副本(默认) docker service create --mode global --name test01 centos:7.6 # 全局节点运行网络模式 PublishMode: ingressSwarmOverlayingress:Overlay的特殊模式,负载均衡(IPVS VIP)