搜索到
463
篇与
的结果
-
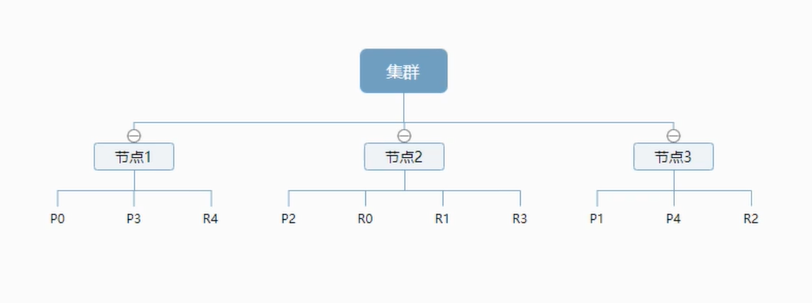
 ElasticSearch相关概念 es与关系型数据库对比Relational DBElastic Search数据库(database)索引(indices)表(table)types(类型)(es8.0弃用)行(rows)documents(文档)字段(columns)fieldses(集群)中可以包含多个索引(数据库),每个索引中可以包含多个类型(表),每个类型下又包含多个文档(行),每个文档又包含多个字段(列)。物理设计:es在后台把每个索引划分成多个分片,每份分片可以在集群中的不同服务器间迁移逻辑设计:一个索引类型中包含多个文档,例如:文档1、文档2,当要搜索一篇文档时,大致流程为:索引 ---> 类型 ---> 文档ID(ID不必是整数,实际上是一个字符串)文档es是面向文档的,也就是说索引和搜索数据的最小单位是文档,其包含有几个重要属性:自我包含,一篇文档同时包含字段和对应的值,即key:value层次型的:一个文档中包含自文档(json对象,fastjson进行自动转换)灵活的结构:文档不依赖预先定义的模式,在关系型数据库中,要提前定义字段才能使用,而在es中,可以忽略一个字段或动态的添加一个新的字段在es中,每个字段的类型非常重要,它会保存字段和类型之间的映射及其他的设置,这种映射具体到每个映射的每种类型,这也是为什么在es中,类型有时候也称为映射类型类型类型是文档的逻辑容器(就像关系型数据库,表格是行的容器),类型中对于字段的定义称为映射,比如name映射为字符串类型。先定义好字段,再使用索引es中的索引就是数据库,索引是映射类型的容器,是一个非常大的文档集合,存储映射类型和其他设置,再被存放到各个分片上物理设计:节点和分片如何工作一个集群至少有一个节点,而一个节点就是一个es进程,创建索引时,默认5个分片(primary shard,主分片),每一个主分片会有一个副本(replica shard,复制分片)以上图3个节点的集群为例,可以看出主分片和对应的复制分片都不会在同一个节点内,可以避免级联故障。实际上,一个分片是一个Lucence索引,一个包含倒排索引的文件目录,倒排索引使得es可以在不扫描全部文档的情况下,检索出需要的内容。倒排索引es使用的是倒排索引结构,采用Lucence倒排索引作为底层。这种结构适用于快速全文搜索,一个索引由文档中所有不同的列表构成,对于每一个词,都有一个包含它的文档列表。例1:现在有两个文档,每个文档包含以下内容:# 文档1 Study every day,good good up to forever # 文档2 To forever,study every day, good good up为了创建倒排索引,先要将每个文档拆分成独立的词(或称为词条、tokens),然后创建一个包含所有不重复的词条的排序列表 文档1文档2Study√×To×√every√√forever√√day√√study×√good√√every√√to√×up√√现在试图搜索to forever,只需要查看包含每个词条的文档 文档1文档2to√×forever√√total21两个文档都匹配,但第一个文档比第二个文档匹配度更高,没有别的条件时,返回这两个包含关键字的文档例2:通过博客标签来搜索博客文章现搜索包含python标签的文章,相较于搜索原始数据,现只需要搜索标签这一栏,即可更快的获取文章id
ElasticSearch相关概念 es与关系型数据库对比Relational DBElastic Search数据库(database)索引(indices)表(table)types(类型)(es8.0弃用)行(rows)documents(文档)字段(columns)fieldses(集群)中可以包含多个索引(数据库),每个索引中可以包含多个类型(表),每个类型下又包含多个文档(行),每个文档又包含多个字段(列)。物理设计:es在后台把每个索引划分成多个分片,每份分片可以在集群中的不同服务器间迁移逻辑设计:一个索引类型中包含多个文档,例如:文档1、文档2,当要搜索一篇文档时,大致流程为:索引 ---> 类型 ---> 文档ID(ID不必是整数,实际上是一个字符串)文档es是面向文档的,也就是说索引和搜索数据的最小单位是文档,其包含有几个重要属性:自我包含,一篇文档同时包含字段和对应的值,即key:value层次型的:一个文档中包含自文档(json对象,fastjson进行自动转换)灵活的结构:文档不依赖预先定义的模式,在关系型数据库中,要提前定义字段才能使用,而在es中,可以忽略一个字段或动态的添加一个新的字段在es中,每个字段的类型非常重要,它会保存字段和类型之间的映射及其他的设置,这种映射具体到每个映射的每种类型,这也是为什么在es中,类型有时候也称为映射类型类型类型是文档的逻辑容器(就像关系型数据库,表格是行的容器),类型中对于字段的定义称为映射,比如name映射为字符串类型。先定义好字段,再使用索引es中的索引就是数据库,索引是映射类型的容器,是一个非常大的文档集合,存储映射类型和其他设置,再被存放到各个分片上物理设计:节点和分片如何工作一个集群至少有一个节点,而一个节点就是一个es进程,创建索引时,默认5个分片(primary shard,主分片),每一个主分片会有一个副本(replica shard,复制分片)以上图3个节点的集群为例,可以看出主分片和对应的复制分片都不会在同一个节点内,可以避免级联故障。实际上,一个分片是一个Lucence索引,一个包含倒排索引的文件目录,倒排索引使得es可以在不扫描全部文档的情况下,检索出需要的内容。倒排索引es使用的是倒排索引结构,采用Lucence倒排索引作为底层。这种结构适用于快速全文搜索,一个索引由文档中所有不同的列表构成,对于每一个词,都有一个包含它的文档列表。例1:现在有两个文档,每个文档包含以下内容:# 文档1 Study every day,good good up to forever # 文档2 To forever,study every day, good good up为了创建倒排索引,先要将每个文档拆分成独立的词(或称为词条、tokens),然后创建一个包含所有不重复的词条的排序列表 文档1文档2Study√×To×√every√√forever√√day√√study×√good√√every√√to√×up√√现在试图搜索to forever,只需要查看包含每个词条的文档 文档1文档2to√×forever√√total21两个文档都匹配,但第一个文档比第二个文档匹配度更高,没有别的条件时,返回这两个包含关键字的文档例2:通过博客标签来搜索博客文章现搜索包含python标签的文章,相较于搜索原始数据,现只需要搜索标签这一栏,即可更快的获取文章id -
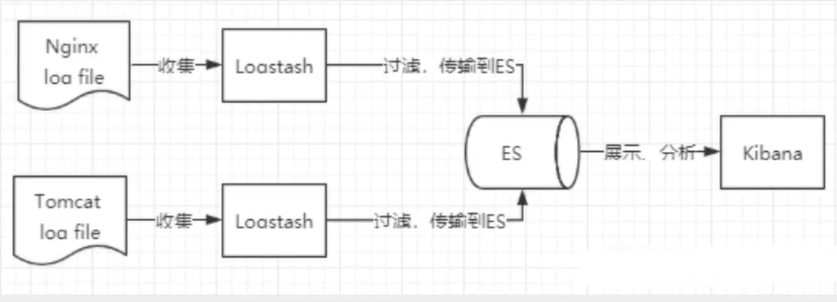
 Elastic Search 一、概述Elastic Search简称es,是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文检索引擎,它可以近乎实时的存储、检索数据,可以使用java开发并使用Lucence作为其核心来实现所有索引和搜索的功能,其目的是通过简单的RESTfull API来隐藏Lucence的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。二、ELKELK是Elastic Search、Logstash、Kibana的首字母简称,也成为Elastic Stack。其中Elastic Search是一个基于Lucence、分布式、通过Restfull方式进行交互的近实时搜索平台框架;Logstash是ELK的中央数据流引擎,用于从不同目标(文件/数据存储/MQ)收集的不同格式数据,经过过滤后支持输出到不同目的地(文件/MQ/rdis/elasticsearch/Kafka等);Kibana可以将elasticsearch的数据通过友好的页面展示出来。提供实时分析的功能。三、安装1、elasticsearch官网地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/elasticsearch/# 跨域问题须在/config/elasticsearch.yml配置文件末尾添加 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"2、Kibana官网地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/kibana注意:es和kibana的版本必须一致
Elastic Search 一、概述Elastic Search简称es,是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文检索引擎,它可以近乎实时的存储、检索数据,可以使用java开发并使用Lucence作为其核心来实现所有索引和搜索的功能,其目的是通过简单的RESTfull API来隐藏Lucence的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。二、ELKELK是Elastic Search、Logstash、Kibana的首字母简称,也成为Elastic Stack。其中Elastic Search是一个基于Lucence、分布式、通过Restfull方式进行交互的近实时搜索平台框架;Logstash是ELK的中央数据流引擎,用于从不同目标(文件/数据存储/MQ)收集的不同格式数据,经过过滤后支持输出到不同目的地(文件/MQ/rdis/elasticsearch/Kafka等);Kibana可以将elasticsearch的数据通过友好的页面展示出来。提供实时分析的功能。三、安装1、elasticsearch官网地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/elasticsearch/# 跨域问题须在/config/elasticsearch.yml配置文件末尾添加 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"2、Kibana官网地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/kibana注意:es和kibana的版本必须一致 -
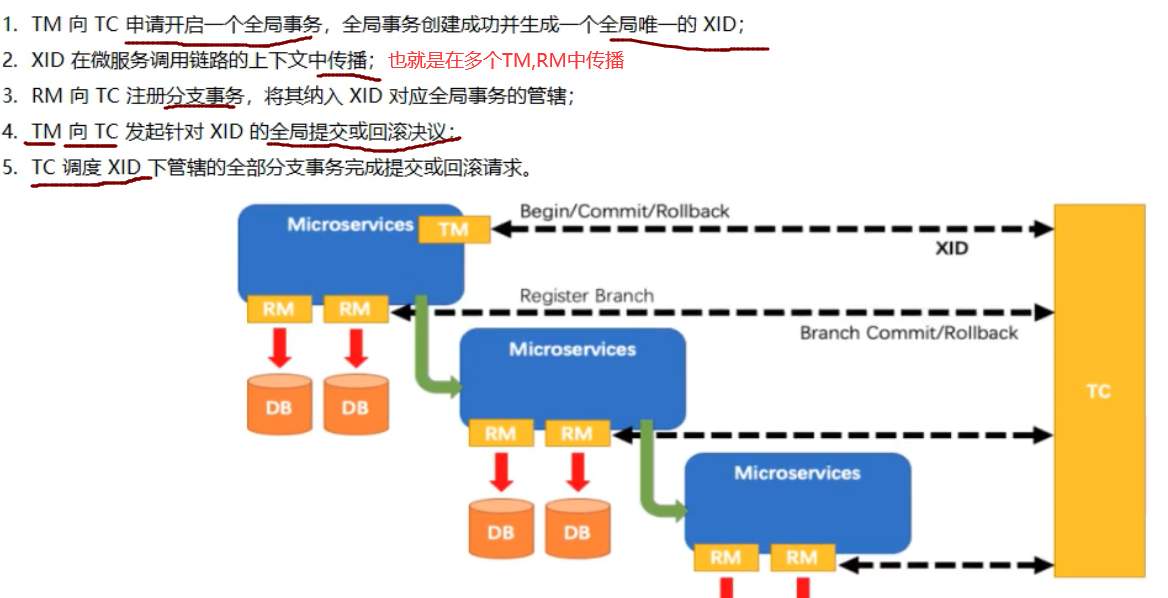
 Seata分布式事务原理 1、TM开启分布式事务(TM向TC注册全局事务)2、按业务场景,编排数据库、服务等事务内的资源(RM向TC汇报资源准备状态)3、TM结束分布式事务,事务一阶段结束(TM通知TC提交/回滚)4、TC汇总事务信息,决定最终是提交还是回滚事务5、TC通知所有RM提交/回滚 资源,事务二阶段结束Seata提供了四个模式:AT、TCC、SAGA、XAAT模式两阶段提交协议的演变:一阶段:业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源二阶段:提交异步化(能快速完成);回滚通过一阶段的回滚日志进行反向补偿一阶段:在一阶段,seata会拦截“业务SQL”:1、解析SQL语义,找到“业务SQL”要更新的业务数据,在业务数据被更新前,将其保存为before image2、执行“业务SQL”更新业务数据,更新之后将业务数据保存为after image3、最后生成行锁以上操作全部在一个数据库事务内完成,保证了一阶段操作的原子性二阶段:1、成功提交二阶段正常执行的话,只需将一阶段保存的快照数据和行锁删除,即可完成数据清理,因为“业务SQl”在一阶段已经在提交至数据库2、事务回滚二阶段如果出现异常,需要事务回滚,seata就需要回滚一阶段已经执行的“业务SQL”,还原业务数据;回滚方式使用before image还原业务数据,在还原之前需要做校验脏写,对比数据库当前的业务数据和after image数据快照,如果两份数据完全一致,就说明没有脏写,执行还原操作,如果不一致,就需要转人工处理
Seata分布式事务原理 1、TM开启分布式事务(TM向TC注册全局事务)2、按业务场景,编排数据库、服务等事务内的资源(RM向TC汇报资源准备状态)3、TM结束分布式事务,事务一阶段结束(TM通知TC提交/回滚)4、TC汇总事务信息,决定最终是提交还是回滚事务5、TC通知所有RM提交/回滚 资源,事务二阶段结束Seata提供了四个模式:AT、TCC、SAGA、XAAT模式两阶段提交协议的演变:一阶段:业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源二阶段:提交异步化(能快速完成);回滚通过一阶段的回滚日志进行反向补偿一阶段:在一阶段,seata会拦截“业务SQL”:1、解析SQL语义,找到“业务SQL”要更新的业务数据,在业务数据被更新前,将其保存为before image2、执行“业务SQL”更新业务数据,更新之后将业务数据保存为after image3、最后生成行锁以上操作全部在一个数据库事务内完成,保证了一阶段操作的原子性二阶段:1、成功提交二阶段正常执行的话,只需将一阶段保存的快照数据和行锁删除,即可完成数据清理,因为“业务SQl”在一阶段已经在提交至数据库2、事务回滚二阶段如果出现异常,需要事务回滚,seata就需要回滚一阶段已经执行的“业务SQL”,还原业务数据;回滚方式使用before image还原业务数据,在还原之前需要做校验脏写,对比数据库当前的业务数据和after image数据快照,如果两份数据完全一致,就说明没有脏写,执行还原操作,如果不一致,就需要转人工处理 -
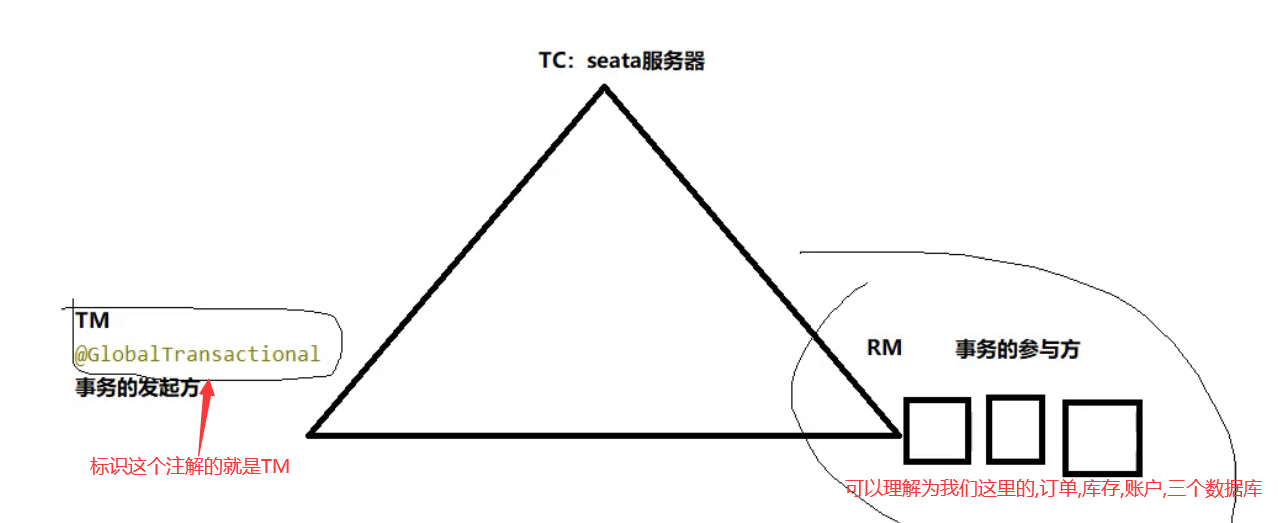
 Seata seata是一个分布式的解决方案,致力于在微服务架构下提供高性能和简单易用的分布式微服务,官网:http://seata.io/zh-cn/一、三组概念TC 事务协调者:维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚TM 事务管理器:定义全局事务的范围:开始、提交、回滚RM 资源管理器:管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚二、安装GitHub地址:https://github.com/seata/seata(以Nacos 2.0、Seata 1.4.2为例)修改配置文件1、/conf/file.conf (注意与1.0之前的版本区分,1.0之后可以在yml文件中指定service配置)修改数据库模式(使用数据库存储事务信息)和数据源2、/conf/registry.conf3、mysql建表1、新建seata数据库2、运行mysql.sql注意:建表sql在/conf/REDME.md文件中,点击server出现存放sql的github地址:https://github.com/seata/seata/tree/develop/script/server4、启动先启动Nacos再启动Seata(bin/seata-server.bat)三、业务测试1、业务说明创建三个微服务:订单---库存---账户大致流程:当用户下单时,订单服务创建订单,远程调用库存服务扣减库存,再通过远程调用账户服务来扣减账户余额,最后在订单服务中修改订单状态为已完成。2、数据库建表创建三个数据库seata_order(订单),seata_storage(库存),seata_account(账户)创建对应的表-- t_order DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_order`; CREATE TABLE `t_order` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `product_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '产品id', `count` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '数量', `money` decimal(11, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '金额', `status` int(1) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '订单状态:0:创建中; 1:已完结', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 14 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- t_storage DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_storage`; CREATE TABLE `t_storage` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `product_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '产品id', `total` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '总库存', `used` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '已用库存', `residue` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '剩余库存', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_storage` VALUES (1, 1, 100, 0, 100); -- t_account DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_account`; CREATE TABLE `t_account` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `user_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `total` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '总额度', `used` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '已用余额', `residue` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '剩余可用额度', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (1, 1, 1000, 0, 1000);undo回滚日志表,三个库每个都需要创建一张回滚表,分别执行三次DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `undo_log`; CREATE TABLE `undo_log` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `xid` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `context` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL, `log_status` int(11) NOT NULL, `log_created` datetime(0) NOT NULL, `log_modified` datetime(0) NOT NULL, `ext` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE INDEX `ux_undo_log`(`xid`, `branch_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;3、seata-order-servicepom<dependencies> <!-- API --> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <!--nacos--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <!--seata--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>seata-all</artifactId> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> <artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> <!--feign--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> <!--web-actuator--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <!--mysql-druid--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies>ymlserver: port: 2001 spring: application: name: seata-order-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata_order?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 username: root password: 123456 seata: enabled: true application-id: ${spring.application.name} # 自定义事务组名称 tx-service-group: test_tx_group service: vgroup-mapping: test_tx_group: default config: nacos: namespace: server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 group: SEATA_GROUP userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" registry: type: nacos nacos: application: seata-server server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 namespace: userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" feign: hystrix: enabled: false logging: level: io: seata: info启动类@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class) //取消自动创建数据源 @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients @MapperScan("com.sw.mapper") public class SeataOrderMain2001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SeataOrderMain2001.class, args); } }pojo@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Order implements Serializable { private Long id; private Long userId; private Long productId; private Integer count; private BigDecimal money; private Integer status; //订单状态:0:创建中;1:已完结 }mapper@Repository public interface OrderMapper { /** * 新建订单 * @param order */ @Insert("insert into t_order(id,user_id,product_id,count,money,status) " + "values(null,#{userId},#{productId},#{count},#{money},0)") void create(Order order); /** * 更新订单 * @param userId * @param status */ @Update("update t_order set status = 1 " + "where user_id=#{userId} and status = #{status}") void update(@Param("userId")Long userId, @Param("status")Integer status); }serviceOrderServicepublic interface OrderService { void create(Order order); }StorageService@FeignClient("seata-storage-service") public interface StorageService { @PostMapping("/storage/decrease") CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("productId")Long productId, @RequestParam("count")Integer count); }AccountService@FeignClient("seata-account-service") public interface AccountService { @PostMapping("/account/decrease") CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("userId")Long userId, @RequestParam("money")BigDecimal money); }service实现@Service @Slf4j public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private OrderMapper orderMapper; @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Autowired private StorageService storageService; @Override public void create(Order order) { //1.新建订单 log.info("===开始新建订单==="); orderMapper.create(order); //2.扣减库存 log.info("===订单微服务调用库存==="); storageService.decrease(order.getProductId(), order.getCount()); log.info("===订单微服务调用库存,库存数量操作结束==="); //3.扣减账户 log.info("===订单微服务调用账户余额==="); accountService.decrease(order.getUserId(), order.getMoney()); log.info("===订单微服务调用账户余额,账户余额操作结束==="); //4.修改订单状态 log.info("===修改订单状态,开始==="); //从 0 到 1,1代表已经完成 orderMapper.update(order.getUserId(), 0); log.info("===修改订单状态,操作结束==="); log.info("订单操作完成(*^_^*)"); } }controller@RestController @RequestMapping("/order") public class OrderController { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; @GetMapping("/create") public CommonResult create(Order order){ orderService.create(order); return new CommonResult(200, "订单创建成功!"); } } config主启动类排除了数据源配置,此处需指定数据源代理@Configuration public class DataSourceProxyConfig { @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") public DataSource druidDataSource(){ return new DruidDataSource(); } @Primary @Bean("dataSource") public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource dataSource){ return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource); } }4、seata-storage-serviceymlserver: port: 2002 spring: application: name: seata-storage-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata_storage?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 username: root password: 123456 seata: enabled: true application-id: ${spring.application.name} tx-service-group: test_tx_group service: vgroup-mapping: test_tx_group: default config: nacos: namespace: server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 group: SEATA_GROUP userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" registry: type: nacos nacos: application: seata-server server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 namespace: userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" feign: hystrix: enabled: false logging: level: io: seata: infomapper@Repository public interface StorageMapper { /** * 扣减库存信息 * @param productId * @param count */ @Update("update t_storage " + "set used = used + #{count}," + "residue = residue - #{count} "+ "where product_id = #{productId}" ) void decrease(@Param("productId")Long productId, @Param("count")Integer count); }servicepublic interface StorageService { void decrease(Long productId, Integer count); }service实现@Slf4j @Service public class StorageServiceImpl implements StorageService { @Autowired private StorageMapper storageMapper; @Override public void decrease(Long productId, Integer count) { log.info("===storage-service 开始扣减库存==="); storageMapper.decrease(productId, count); log.info("===storage-service 扣减库存操作结束==="); } }其他配置同理order微服务模块的5、seata-account-servicemapper@Repository public interface AccountMapper { /** * 扣减账户余额 * @param userId * @param money */ @Update("update t_account set "+ "used = used + #{money},"+ "residue = residue - #{money} "+ "where user_id = #{userId}" ) void decrease(@Param("userId")Long userId, @Param("money") BigDecimal money); }其他配置同理storage微服务模块的创建6、不添加全局事务管理测试seata-account-service模块1、手动模拟超时@Slf4j @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountMapper accountMapper; @Override public void decrease(Long userId, BigDecimal money) { log.info("===account-service 开始扣减账户余额==="); //模拟超时异常 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } accountMapper.decrease(userId, money); log.info("===account-service 扣减账户余额操作结束==="); } }浏览器输入http://localhost:2001/order/create?userId=1&productId=1&count=10&money=100报错Read TimeOut异常:此时数据库的状态:7、开启全局事务在order模块中添加全局事务注解@GlobalTransactional使用同样的方法测试,发生调用超时异常后,数据库中被修改的数据回滚到了操作之前的状态
Seata seata是一个分布式的解决方案,致力于在微服务架构下提供高性能和简单易用的分布式微服务,官网:http://seata.io/zh-cn/一、三组概念TC 事务协调者:维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚TM 事务管理器:定义全局事务的范围:开始、提交、回滚RM 资源管理器:管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚二、安装GitHub地址:https://github.com/seata/seata(以Nacos 2.0、Seata 1.4.2为例)修改配置文件1、/conf/file.conf (注意与1.0之前的版本区分,1.0之后可以在yml文件中指定service配置)修改数据库模式(使用数据库存储事务信息)和数据源2、/conf/registry.conf3、mysql建表1、新建seata数据库2、运行mysql.sql注意:建表sql在/conf/REDME.md文件中,点击server出现存放sql的github地址:https://github.com/seata/seata/tree/develop/script/server4、启动先启动Nacos再启动Seata(bin/seata-server.bat)三、业务测试1、业务说明创建三个微服务:订单---库存---账户大致流程:当用户下单时,订单服务创建订单,远程调用库存服务扣减库存,再通过远程调用账户服务来扣减账户余额,最后在订单服务中修改订单状态为已完成。2、数据库建表创建三个数据库seata_order(订单),seata_storage(库存),seata_account(账户)创建对应的表-- t_order DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_order`; CREATE TABLE `t_order` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `product_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '产品id', `count` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '数量', `money` decimal(11, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '金额', `status` int(1) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '订单状态:0:创建中; 1:已完结', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 14 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- t_storage DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_storage`; CREATE TABLE `t_storage` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `product_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '产品id', `total` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '总库存', `used` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '已用库存', `residue` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '剩余库存', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_storage` VALUES (1, 1, 100, 0, 100); -- t_account DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_account`; CREATE TABLE `t_account` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `user_id` bigint(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `total` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '总额度', `used` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '已用余额', `residue` decimal(10, 0) NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '剩余可用额度', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (1, 1, 1000, 0, 1000);undo回滚日志表,三个库每个都需要创建一张回滚表,分别执行三次DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `undo_log`; CREATE TABLE `undo_log` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `xid` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `context` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL, `log_status` int(11) NOT NULL, `log_created` datetime(0) NOT NULL, `log_modified` datetime(0) NOT NULL, `ext` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE INDEX `ux_undo_log`(`xid`, `branch_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;3、seata-order-servicepom<dependencies> <!-- API --> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <!--nacos--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <!--seata--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>seata-all</artifactId> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> <artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> <!--feign--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> <!--web-actuator--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <!--mysql-druid--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies>ymlserver: port: 2001 spring: application: name: seata-order-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata_order?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 username: root password: 123456 seata: enabled: true application-id: ${spring.application.name} # 自定义事务组名称 tx-service-group: test_tx_group service: vgroup-mapping: test_tx_group: default config: nacos: namespace: server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 group: SEATA_GROUP userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" registry: type: nacos nacos: application: seata-server server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 namespace: userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" feign: hystrix: enabled: false logging: level: io: seata: info启动类@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class) //取消自动创建数据源 @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients @MapperScan("com.sw.mapper") public class SeataOrderMain2001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SeataOrderMain2001.class, args); } }pojo@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Order implements Serializable { private Long id; private Long userId; private Long productId; private Integer count; private BigDecimal money; private Integer status; //订单状态:0:创建中;1:已完结 }mapper@Repository public interface OrderMapper { /** * 新建订单 * @param order */ @Insert("insert into t_order(id,user_id,product_id,count,money,status) " + "values(null,#{userId},#{productId},#{count},#{money},0)") void create(Order order); /** * 更新订单 * @param userId * @param status */ @Update("update t_order set status = 1 " + "where user_id=#{userId} and status = #{status}") void update(@Param("userId")Long userId, @Param("status")Integer status); }serviceOrderServicepublic interface OrderService { void create(Order order); }StorageService@FeignClient("seata-storage-service") public interface StorageService { @PostMapping("/storage/decrease") CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("productId")Long productId, @RequestParam("count")Integer count); }AccountService@FeignClient("seata-account-service") public interface AccountService { @PostMapping("/account/decrease") CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("userId")Long userId, @RequestParam("money")BigDecimal money); }service实现@Service @Slf4j public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private OrderMapper orderMapper; @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Autowired private StorageService storageService; @Override public void create(Order order) { //1.新建订单 log.info("===开始新建订单==="); orderMapper.create(order); //2.扣减库存 log.info("===订单微服务调用库存==="); storageService.decrease(order.getProductId(), order.getCount()); log.info("===订单微服务调用库存,库存数量操作结束==="); //3.扣减账户 log.info("===订单微服务调用账户余额==="); accountService.decrease(order.getUserId(), order.getMoney()); log.info("===订单微服务调用账户余额,账户余额操作结束==="); //4.修改订单状态 log.info("===修改订单状态,开始==="); //从 0 到 1,1代表已经完成 orderMapper.update(order.getUserId(), 0); log.info("===修改订单状态,操作结束==="); log.info("订单操作完成(*^_^*)"); } }controller@RestController @RequestMapping("/order") public class OrderController { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; @GetMapping("/create") public CommonResult create(Order order){ orderService.create(order); return new CommonResult(200, "订单创建成功!"); } } config主启动类排除了数据源配置,此处需指定数据源代理@Configuration public class DataSourceProxyConfig { @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") public DataSource druidDataSource(){ return new DruidDataSource(); } @Primary @Bean("dataSource") public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource dataSource){ return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource); } }4、seata-storage-serviceymlserver: port: 2002 spring: application: name: seata-storage-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata_storage?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 username: root password: 123456 seata: enabled: true application-id: ${spring.application.name} tx-service-group: test_tx_group service: vgroup-mapping: test_tx_group: default config: nacos: namespace: server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 group: SEATA_GROUP userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" registry: type: nacos nacos: application: seata-server server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 namespace: userName: "nacos" password: "nacos" feign: hystrix: enabled: false logging: level: io: seata: infomapper@Repository public interface StorageMapper { /** * 扣减库存信息 * @param productId * @param count */ @Update("update t_storage " + "set used = used + #{count}," + "residue = residue - #{count} "+ "where product_id = #{productId}" ) void decrease(@Param("productId")Long productId, @Param("count")Integer count); }servicepublic interface StorageService { void decrease(Long productId, Integer count); }service实现@Slf4j @Service public class StorageServiceImpl implements StorageService { @Autowired private StorageMapper storageMapper; @Override public void decrease(Long productId, Integer count) { log.info("===storage-service 开始扣减库存==="); storageMapper.decrease(productId, count); log.info("===storage-service 扣减库存操作结束==="); } }其他配置同理order微服务模块的5、seata-account-servicemapper@Repository public interface AccountMapper { /** * 扣减账户余额 * @param userId * @param money */ @Update("update t_account set "+ "used = used + #{money},"+ "residue = residue - #{money} "+ "where user_id = #{userId}" ) void decrease(@Param("userId")Long userId, @Param("money") BigDecimal money); }其他配置同理storage微服务模块的创建6、不添加全局事务管理测试seata-account-service模块1、手动模拟超时@Slf4j @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountMapper accountMapper; @Override public void decrease(Long userId, BigDecimal money) { log.info("===account-service 开始扣减账户余额==="); //模拟超时异常 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } accountMapper.decrease(userId, money); log.info("===account-service 扣减账户余额操作结束==="); } }浏览器输入http://localhost:2001/order/create?userId=1&productId=1&count=10&money=100报错Read TimeOut异常:此时数据库的状态:7、开启全局事务在order模块中添加全局事务注解@GlobalTransactional使用同样的方法测试,发生调用超时异常后,数据库中被修改的数据回滚到了操作之前的状态 -
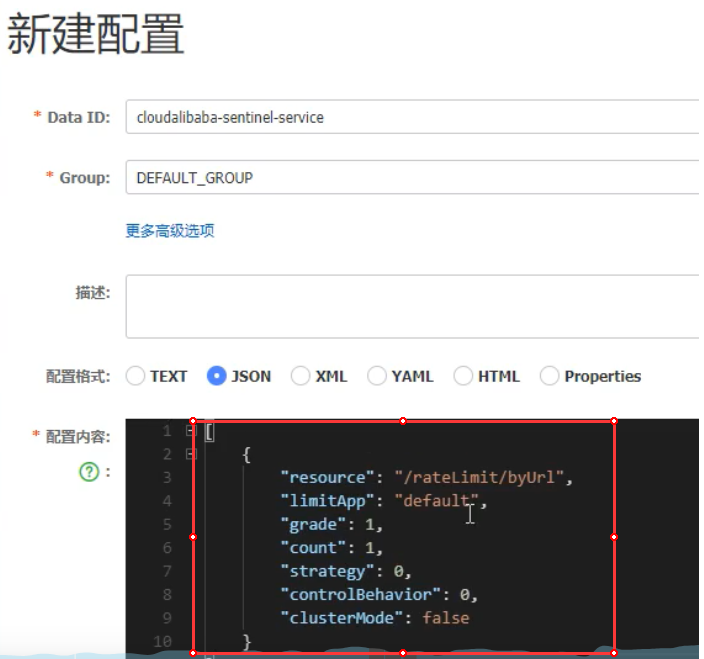
 Sentinel规则持久化 默认规则是临时存储的,重启Sentinel服务之后消失1、环境搭建以8401模块为例添加pom依赖<!-- datasource-nacos --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId> </dependency>ymlserver: port: 8401 spring: application: name: cloud-alibaba-sentinel-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 sentinel: transport: # sentinel dashboard地址 dashboard: localhost:8080 # 默认8719端口,如果8719被占用,默认递增 port: 8719 # 流控规则持久化 datasource: ds1: nacos: server-addr: localhost:8848 # namespace根据具体的情况指定 dataId: cloud-alibaba-sentinel-service groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: flow management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'Nacos新建配置文件参数说明:resource:资源名称limitApp:应用来源grade:阈值类型,0:线程数,1:QPScount:单机阈值strategy:流控模式,0:直接,1:关联,2:链路controBehavier:流控效果,0:快速失败,1:Warm Up,2:排队等待clusterMode:是否集群2、测试1、启动8401,在Sentinel控制中心可以看到读取了Nacos那边配置的流控规则;2、关闭8401,Sentinel控制中心的规则消失;3、重启8401,重启之后如果出现了流控规则,则表明规则持久化配置成功。图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba
Sentinel规则持久化 默认规则是临时存储的,重启Sentinel服务之后消失1、环境搭建以8401模块为例添加pom依赖<!-- datasource-nacos --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId> </dependency>ymlserver: port: 8401 spring: application: name: cloud-alibaba-sentinel-service cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 sentinel: transport: # sentinel dashboard地址 dashboard: localhost:8080 # 默认8719端口,如果8719被占用,默认递增 port: 8719 # 流控规则持久化 datasource: ds1: nacos: server-addr: localhost:8848 # namespace根据具体的情况指定 dataId: cloud-alibaba-sentinel-service groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: flow management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'Nacos新建配置文件参数说明:resource:资源名称limitApp:应用来源grade:阈值类型,0:线程数,1:QPScount:单机阈值strategy:流控模式,0:直接,1:关联,2:链路controBehavier:流控效果,0:快速失败,1:Warm Up,2:排队等待clusterMode:是否集群2、测试1、启动8401,在Sentinel控制中心可以看到读取了Nacos那边配置的流控规则;2、关闭8401,Sentinel控制中心的规则消失;3、重启8401,重启之后如果出现了流控规则,则表明规则持久化配置成功。图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba -
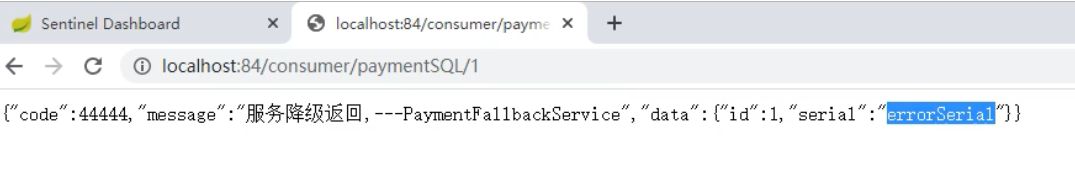
 Sentinel整合Open Feign 1、环境搭建以8884模块为例pom文件添加依赖<!-- openfign --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency>yml添加# 激活sentinel对feign的支持 feign: sentinel: enabled: true启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients public class OrderMain84 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain84.class, args); } }创建远程调用接口@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider") public interface PaymentService { @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id); }实现类(用于服务降级)@Component public class PaymentFallbackService implements PaymentService { @Override public CommonResult<Payment> payment(Long id) { return new CommonResult<Payment>(444, "服务降级返回--PaymentService", new Payment(id, "errorSerial")); } }接口指定降级的类@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider", fallback = PaymentFallbackService.class) public interface PaymentService { @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id); }controller@Resource private PaymentService service; @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ return service.payment(id); }2、测试启动9003、8884,如果中途9003出现问题关闭,8884服务降级成功3、熔断框架比较 SentinelHystrixresilience4j隔离策略信号量隔离线程池/信号量隔离信号量隔离熔断降级策略基于响应时间、异常比例、异常数异常比例异常比例、响应时间实时统计滑动窗口(LeapArray)滑动窗口(Rxjava)Ring Bit Buffer动态规则支持多种数据源支持多种数据源有限的支持扩展性多个扩展点插件接口基于注解的支持支持支持支持限流QPS、调用关系有限的支持Rate Limiter图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba
Sentinel整合Open Feign 1、环境搭建以8884模块为例pom文件添加依赖<!-- openfign --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency>yml添加# 激活sentinel对feign的支持 feign: sentinel: enabled: true启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients public class OrderMain84 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain84.class, args); } }创建远程调用接口@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider") public interface PaymentService { @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id); }实现类(用于服务降级)@Component public class PaymentFallbackService implements PaymentService { @Override public CommonResult<Payment> payment(Long id) { return new CommonResult<Payment>(444, "服务降级返回--PaymentService", new Payment(id, "errorSerial")); } }接口指定降级的类@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider", fallback = PaymentFallbackService.class) public interface PaymentService { @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id); }controller@Resource private PaymentService service; @GetMapping("/payment/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ return service.payment(id); }2、测试启动9003、8884,如果中途9003出现问题关闭,8884服务降级成功3、熔断框架比较 SentinelHystrixresilience4j隔离策略信号量隔离线程池/信号量隔离信号量隔离熔断降级策略基于响应时间、异常比例、异常数异常比例异常比例、响应时间实时统计滑动窗口(LeapArray)滑动窗口(Rxjava)Ring Bit Buffer动态规则支持多种数据源支持多种数据源有限的支持扩展性多个扩展点插件接口基于注解的支持支持支持支持限流QPS、调用关系有限的支持Rate Limiter图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba -
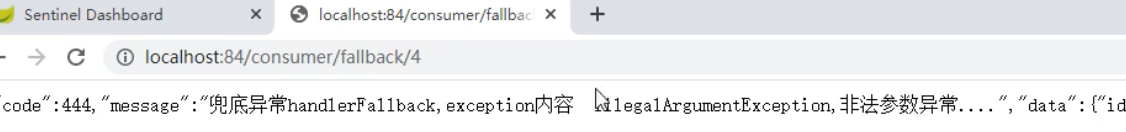
 服务熔断 1、环境搭建1、启动Nacos、Sentinel2、新建9003、9004两个模块pom<!-- API --> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <!-- Nacos --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>ymlserver: port: 9003 spring: application: name: nacos-payment-provider cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class PaymentMain9003 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain9003.class, args); } }controller(此处的虚拟数据库是为了方便演示)@RestController @RequestMapping("/payment") public class PaymentController { @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; public static Map<Long, Payment> map = new HashMap<>(); static { map.put(1L, new Payment(1L, "螺蛳粉01")); map.put(2L, new Payment(2L, "螺蛳粉02")); map.put(3L, new Payment(3L, "螺蛳粉03")); } @GetMapping("/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ Payment payment = map.get(id); CommonResult<Payment> result = new CommonResult<>(200, "serverPort: " + serverPort, payment); return result; } }注:9004构建步骤与9003一致2、新建8884模块pom同理9004、9004模块ymlserver: port: 8884 spring: application: name: nacos-order-consumer cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 sentinel: transport: # sentinel dashboard地址 dashboard: localhost:8080 # 默认8719端口,如果8719被占用,默认递增 port: 8719 service-url: nacos-user-service: http://nacos-payment-provider management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class OrderMain84 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain84.class, args); } }config配置类@Configuration public class ApplicationContextConfig { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } }controller@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource("fallback") public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } }指定降级方法@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } }2、测试启动测试:注:此处没有使用Sentinel来配置降级规则,但却降级成功,是因为fallback用于管理异常,当业务发生异常时,可以降级到指定的方法为业务添加blockhandler@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } // public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ // Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); // return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); // } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } }测试结果:注:可以看到返回结果直接报错,并没有降级,所以说blockHandler只适用于Sentinel配置的规则同时配置fallback和blockHandler@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } } 配置Sentinel规则:结果:可以看到,同时配置fallback和blockHandler,blockHandler的优先级更高exceptionsToIgnore属性@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler", exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalArgumentException.class}) public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } }测试结果:注:使用exceptionsToIgnore指定异常类,表示当前方法如果抛出了指定的异常,不进行降级处理,直接返回抛出的异常结果图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba
服务熔断 1、环境搭建1、启动Nacos、Sentinel2、新建9003、9004两个模块pom<!-- API --> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <!-- Nacos --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>ymlserver: port: 9003 spring: application: name: nacos-payment-provider cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class PaymentMain9003 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain9003.class, args); } }controller(此处的虚拟数据库是为了方便演示)@RestController @RequestMapping("/payment") public class PaymentController { @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; public static Map<Long, Payment> map = new HashMap<>(); static { map.put(1L, new Payment(1L, "螺蛳粉01")); map.put(2L, new Payment(2L, "螺蛳粉02")); map.put(3L, new Payment(3L, "螺蛳粉03")); } @GetMapping("/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> payment(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ Payment payment = map.get(id); CommonResult<Payment> result = new CommonResult<>(200, "serverPort: " + serverPort, payment); return result; } }注:9004构建步骤与9003一致2、新建8884模块pom同理9004、9004模块ymlserver: port: 8884 spring: application: name: nacos-order-consumer cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: localhost:8848 sentinel: transport: # sentinel dashboard地址 dashboard: localhost:8080 # 默认8719端口,如果8719被占用,默认递增 port: 8719 service-url: nacos-user-service: http://nacos-payment-provider management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class OrderMain84 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain84.class, args); } }config配置类@Configuration public class ApplicationContextConfig { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } }controller@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource("fallback") public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } }指定降级方法@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } }2、测试启动测试:注:此处没有使用Sentinel来配置降级规则,但却降级成功,是因为fallback用于管理异常,当业务发生异常时,可以降级到指定的方法为业务添加blockhandler@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } // public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ // Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); // return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); // } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } }测试结果:注:可以看到返回结果直接报错,并没有降级,所以说blockHandler只适用于Sentinel配置的规则同时配置fallback和blockHandler@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } } 配置Sentinel规则:结果:可以看到,同时配置fallback和blockHandler,blockHandler的优先级更高exceptionsToIgnore属性@RestController @RequestMapping("/consumer") public class CircleBreakerController { public static final String SERVICE_URL = "http://nacos-payment-provider"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "fallback/{id}", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) //@SentinelResource("fallback") //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback只负责业务异常 //@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台的配置 @SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler", exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalArgumentException.class}) public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/payment/" + id, CommonResult.class, id); if (id ==4){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常!"); }else if (result.getData() == null){ throw new NullPointerException("没有找到对应id的记录!"); } return result; } public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable("id")Long id, Throwable e){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"handlerFallback,异常内容:" + e.getMessage(), payment); } public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable("id")Long id, BlockException exception){ Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null"); return new CommonResult(444,"blockHandler,异常内容:" + exception.getMessage(), payment); } }测试结果:注:使用exceptionsToIgnore指定异常类,表示当前方法如果抛出了指定的异常,不进行降级处理,直接返回抛出的异常结果图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba -
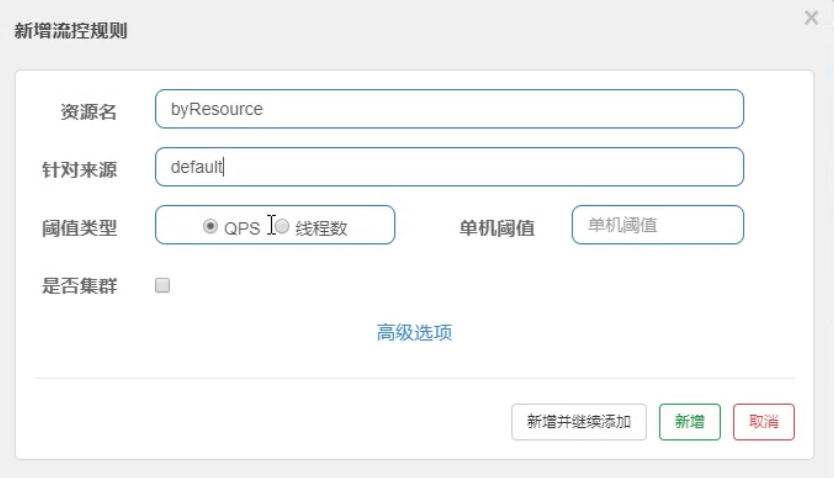
 @SentinelResource注解 1、环境搭建(8401模块)8401模块的pom增加以下依赖<!--通用Commons--> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>controller@RestController public class RateLimitController { @GetMapping(value = "/byResource", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource(value = "byResource", blockHandler = "handlerException") public CommonResult<JSONObject> byResource(){ return new CommonResult(200, "按资源名称测试限流",new Payment(100L, "干脆面")); } public CommonResult<JSONObject> handlerException(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, exception.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "\t 服务不可用!"); } }限流规则注:配置了@SentinelResource注解后,资源名填byResource或者/byResource都可以测试2、自定义限流规则单独创建一个handler类,用于处理限流public class CustomerBlockHandler { public static CommonResult handlerException1(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, "global handlerException01"); } public static CommonResult handlerException2(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, "global handlerException02"); } }controller指定自定义的降级方法@GetMapping(value = "/customerBlockHandler", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource(value = "customerBlockHandler", blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class, blockHandler = "handlerException2" ) public CommonResult<JSONObject> customerBlockHandler(){ return new CommonResult(200, "按客户自定义测试限流",new Payment(100L, "干脆面")); }Sentinel自定义限流规则测试补充3、其他属性@SentinelResource不适用于private方法value:资源名称,必需项(不能为空);entryType:entry类型,可选项(默认为 EntryType.OUT);fallback:fallback函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback处理逻辑;fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback函数签名和位置要求: 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable类型的参数用于接收对应的异常;fallback函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static函数,否则无法解析。 defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):默认的 fallback函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback逻辑(即可以用于很多服务或方法)。默认 fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback会生效。defaultFallback函数签名要求:返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要为空,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常;defaultFallback函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析;exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba
@SentinelResource注解 1、环境搭建(8401模块)8401模块的pom增加以下依赖<!--通用Commons--> <dependency> <groupId>com.sw</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>controller@RestController public class RateLimitController { @GetMapping(value = "/byResource", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource(value = "byResource", blockHandler = "handlerException") public CommonResult<JSONObject> byResource(){ return new CommonResult(200, "按资源名称测试限流",new Payment(100L, "干脆面")); } public CommonResult<JSONObject> handlerException(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, exception.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "\t 服务不可用!"); } }限流规则注:配置了@SentinelResource注解后,资源名填byResource或者/byResource都可以测试2、自定义限流规则单独创建一个handler类,用于处理限流public class CustomerBlockHandler { public static CommonResult handlerException1(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, "global handlerException01"); } public static CommonResult handlerException2(BlockException exception){ return new CommonResult(444, "global handlerException02"); } }controller指定自定义的降级方法@GetMapping(value = "/customerBlockHandler", produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"}) @SentinelResource(value = "customerBlockHandler", blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class, blockHandler = "handlerException2" ) public CommonResult<JSONObject> customerBlockHandler(){ return new CommonResult(200, "按客户自定义测试限流",new Payment(100L, "干脆面")); }Sentinel自定义限流规则测试补充3、其他属性@SentinelResource不适用于private方法value:资源名称,必需项(不能为空);entryType:entry类型,可选项(默认为 EntryType.OUT);fallback:fallback函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback处理逻辑;fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback函数签名和位置要求: 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable类型的参数用于接收对应的异常;fallback函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static函数,否则无法解析。 defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):默认的 fallback函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback逻辑(即可以用于很多服务或方法)。默认 fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback会生效。defaultFallback函数签名要求:返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要为空,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常;defaultFallback函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析;exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。图片来源:尚硅谷 - 周阳 - Spring Cloud Alibaba